What is First Trimester Screening?
First Trimester Screening (FTS) is an early pregnancy check done between 12 to 13 weeks to see if the baby might have certain genetic or chromosomal conditions. It’s like a health check-up for the baby, done before many physical changes show up. The goal is to identify babies at higher risk for problems, early ; so parents and doctors can prepare or do more detailed tests if needed.
Why is it done?
It helps estimate the chance that the baby might have conditions like Down syndrome (extra chromosome 21), Edwards syndrome (extra chromosome 18), or Patau syndrome (extra chromosome 13). It can also signal risks for other problems, like heart defects or genetic syndromes, though it doesn’t detect all birth defects. This early screening helps parents and doctors decide if further testing or special care is needed during the pregnancy.
What are the tests included in First-Trimester Screening?
FTS combines an Ultrasound Scan with some specific blood tests done around the end of the first trimester:
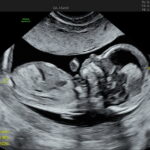
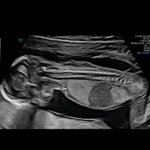
Fetal Nuchal Translucency Ultrasound Scan (12-13weeks): The NT scan checks the thickness of the fluid at the back of the baby’s neck, called nuchal translucency. Too much fluid here can be a sign that something might be wrong.
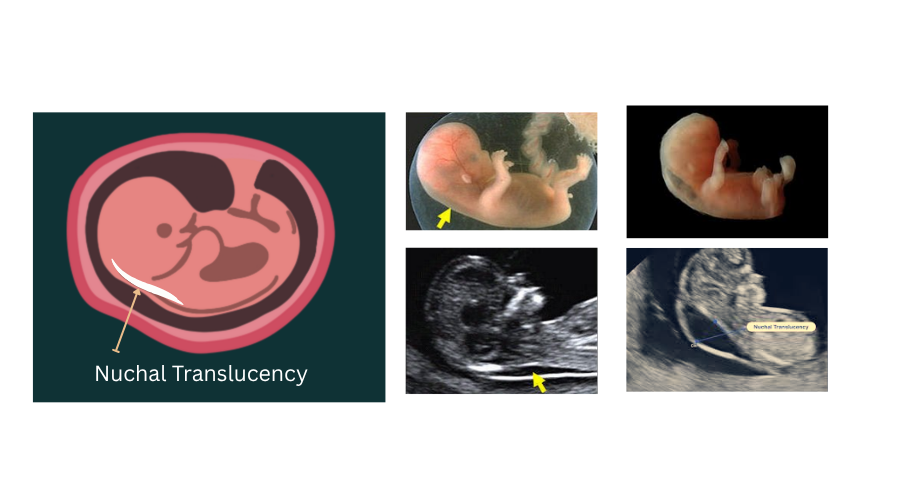
Blood Test: The mother’s blood is tested for two important proteins — Free beta-hCG & PAPP-A. The levels of these proteins can hint at the possibility of chromosomal problems in the baby.
In First Trimester Screening (FTS), two important blood markers are measured to help assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in the baby. These are:
1. Free Beta-hCG (Free Beta Human Chorionic Gonadotropin)
- This is a hormone produced by the placenta shortly after conception.
- It exists in two parts, and the “free beta” subunit is measured in the blood.
- In pregnancies affected by Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), free beta-hCG levels tend to be higher than normal during the first trimester.
- The hormone helps maintain the pregnancy and supports the development of the fetus and placenta.
- High or abnormal levels can indicate a higher chance of chromosomal disorders or other pregnancy complications.[1][3][6]
2. PAPP-A (Pregnancy-Associated Plasma Protein A)
- PAPP-A is a protein also produced by the placenta and is involved in helping the placenta grow and function properly.
- It plays a key role in fetal development and placental health.
- In pregnancies with chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome, PAPP-A levels are typically lower than normal in the first trimester.
- Low levels may also be linked to other pregnancy complications like preeclampsia or growth restrictions, so monitoring this protein gives insight into overall pregnancy health.[4][5][1]
How these markers work together in FTS
The blood levels of free beta-hCG and PAPP-A are combined with the ultrasound measurement of the nuchal translucency (fluid at the back of the baby’s neck) and the mother’s age to calculate the risk of common chromosomal conditions such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, and Patau syndrome. By looking at increased or decreased levels of these markers, doctors can estimate how likely it is that the baby has a genetic condition, helping to guide further decisions on testing or care
In simple terms, free beta-hCG and PAPP-A are early warning signs in the blood that let doctors know if the baby might need closer monitoring or special tests to ensure a healthy pregnancy and safe delivery.
Sometimes, a special blood test called cell-free fetal DNA (cfDNA) test is also done. This test looks directly at the baby’s DNA circulating in the mother’s blood to spot some chromosome issues more accurately.
How does the report help analyze risk?
The screening results are combined with the mother’s age to calculate a “risk score” — for example, 1 in 250 or 1 in 1,300 chance that the baby might have a chromosomal condition. A higher risk score means additional tests, like a chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis, might be recommended to confirm if the baby actually has the condition. It’s important to know FTS is not a diagnosis but a way to identify who might need further testing. Many babies with “higher risk” scores are perfectly healthy.
What are the conditions that the First Trimester Screening Test can detect?
Common Chromosomal Abnormalities Detected by First Trimester Screening Test include:
- Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21): This is the most common chromosomal disorder identified via an increased NT measurement. It is associated with intellectual disability and certain physical features and health concerns in affected children.
- Edwards Syndrome (Trisomy 18): This condition is characterized by severe developmental delays and various structural abnormalities. It often leads to significant complications and a reduced lifespan.
- Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13): Fetuses with this abnormality frequently have severe intellectual and physical impairment as well as a high risk of early mortality.
- Turner Syndrome (Monosomy X, 45,X): This condition affects females and is associated with short stature, heart defects, and infertility.
- Klinefelter Syndrome (47,XXY): This sex chromosome abnormality affects males, causing tall stature, reduced fertility, and sometimes learning difficulties.
- Other Sex Chromosome Abnormalities: These include 47,XXX and 47,XYY, which may be associated with mild physical or developmental features, often detected when increased NT prompts further genetic testing.
- Triploidy: A rare abnormality in which a fetus has three copies of every chromosome instead of two, usually resulting in miscarriage or very poor prognosis.
- Copy Number Variations (CNVs): Occasionally, the NT scan can lead to the detection of genetic microdeletions or microduplications, which are further clarified through specialized testing after abnormal NT findings.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
- Noonan Syndrome and Other Genetic Syndromes: While most commonly associated with chromosomal abnormalities, a highly increased NT can rarely be linked to single-gene syndromes such as Noonan syndrome.isuog
Conclusion:
In summary, FTS is a safe, non-invasive way to obtain important early information about the baby’s health and plan ahead if needed. It can help screen for risk of trisomies and other chromosomal abnormalities. It gives peace of mind to many and a chance for early support if any issues are spotted.
NESA Institute of Fetal Medicine offers the most reliable First Trimester Screening Test in Kolkata at affordable costs. To know more about the First-trimester Screening Test cost, contact our counsellors.